
Thus, the engineer should be wary about using the model to make generalizations beyond the sample data. The imprecision may be due to the small size of the groups. One-way ANOVA example As a crop researcher, you want to test the effect of three different fertilizer mixtures on crop yield. One way ANOVA assumes that each group comes from an approximately normal distribution and that the variability within the groups is roughly constant.

The low predicted R 2 value indicates that the model generates imprecise predictions for new observations. A one-way ANOVA uses one independent variable, while a two-way ANOVA uses two independent variables. The confidence intervals for the remaining pairs of means all include zero, which indicates that the differences are not significant. The engineer can use this estimate of the difference to determine whether the difference is practically significant. The data came from an experiment that was conducted to determine how six. This range does not include zero, which indicates that the difference between these means is significant. This example is based on a data set presented in Milliken and Johnson (1992, p. The graph and the table that include the Tukey simultaneous confidence intervals show that the confidence interval for the difference between the means of Blend 2 and 4 is 3.114 to 15.886. All samples are randomly selected and independent. The engineer uses the Tukey comparison results to formally test whether the difference between a pair of groups is statistically significant. Learning Outcomes Each population from which a sample is taken is assumed to be normal.

The engineer knows that some of the group means are different. This result indicates that the mean differences between the hardness of the paint blends is statistically significant.
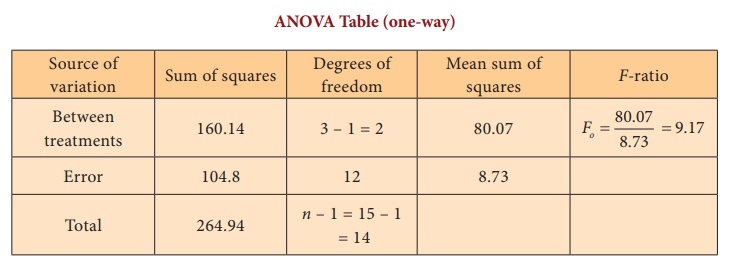
The p-value for the paint hardness ANOVA is less than 0.05.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
